Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques have proven to be effective in enhancing LLMs response quality, particularly in specialized domains. While many RAG approaches have been proposed, most of them still suffer from their complex implementation and prolonged response times.
So what are the best practices in Retrieval-Augmented Generation ?
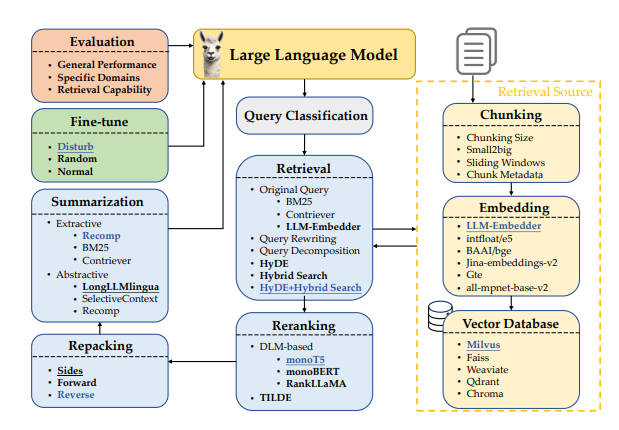
Before we answer this let’s understand a typical RAG workflow, which mainly consists of following. Query Classification : Classify queries to determine the necessity of retrieval. Queries requiring retrieval proceed through the RAG modules; others are handled directly by LLMs.
Chunking : Chunk documents into smaller segments and is crucial for enhancing retrieval precision and avoiding length issues in LLMs. Below are the widely used chunking methods * Token-level Chunking is straightforward but may split sentences, affecting retrieval quality. * Semantic-level Chunking uses LLMs to determine breakpoints, context-preserving but time consuming. * Sentence-level Chunking balances preserving text semantics with simplicity and efficiency
Chunk Size : Larger chunks provide more context, enhancing comprehension but increasing process time. Smaller chunks improve retrieval recall and reduce time but may lack sufficient context. Typical sizes are 2048, 1024, 512, 256 and 128.
Chunking Techniques : like small-to-big and sliding windows improve retrieval quality by organizing chunk block relationships. Small-sized blocks are used to match queries, and larger blocks that include the small ones along with contextual information are returned.
Embedding Model : is crucial for effective semantic matching of queries and chunk blocks.
Metadata Addition : Enhancing chunk blocks with metadata like titles, keywords, and hypothetical questions can improve retrieval during hybrid search.
Vector Databases : store embedding vectors with their metadata, enabling efficient retrieval of documents relevant to queries through various indexing and ANN methods. Vector DB is usually selected based on four key criteria: multiple index types, billion-scale vector support, hybrid search, and cloud-native capabilities
Retrieval Methods : Given a user query, the retrieval module selects the top-k relevant documents from a pre-built corpus based on the similarity between the query and the documents . Following 3 query retrieval method is used
Query Rewriting: refines queries to better match relevant documents. Inspired by the * Query Decomposition: retrieving documents based on sub-questions derived from the original query. * Pseudo-documents Generation: generates a hypothetical document based on the user query and uses the embedding of hypothetical answers to retrieve similar documents e.g. HyDE Combination of above method is also used such as HyDE with Different Concatenation of Documents and Query and Hybrid Search with Different Weight on Sparse Retrieval
Reranking Methods : enhance the relevance of the retrieved documents, ensuring that the most pertinent information appears at the top of the list. Two approaches are widely used * DLM Reranking: leverages deep language models (DLMs) for reranking * TILDE Reranking: calculates the likelihood of each query term independently by predicting token probabilities across the model’s vocabulary.
Document Repacking : module rearranged document after reranking using three methods: Forward method repacks documents by descending relevancy scores from the reranking phase. Reverse arranges them in ascending order and Slide placed at the head or tail of the input.
Summarization : retrieved documents are crucial in the RAG pipeline. Summarization tasks can be Extractive, which segment text into sentences, then score and rank them based on importance or Abstractive, which compressors synthesize information from multiple documents to rephrase and generate a cohesive summary. Recomp, LongLLMLingua and Selective Context are some of the widely used methods.
Searching for Best RAG Practices : * Query Classification Module: This module is referenced and contributes to both effectiveness and efficiency * Retrieval Module: “Hybrid” or “Original” methods are recommended, as they reduce latency while maintaining comparable performance. * Reranking Module: enhancing the quality of generated responses. * Repacking Module: The Reverse configuration exhibited superior performance * Summarization Module: Recomp demonstrated superior performance,
The experimental results demonstrate that each module contributes uniquely to the overall performance of the RAG system. The query classification module enhances accuracy and reduces latency, while the retrieval and reranking modules significantly improve the system’s ability to handle diverse queries. The repacking and summarization modules further refine the system’s output, ensuring high-quality responses across different tasks.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.01219